Distributed fiber optic is a security monitoring system based on fiber optic sensing technology, which uses fiber optic as a sensor and transmission medium to achieve real-time monitoring and alarm of long-distance targets. This technology has advantages such as high sensitivity, strong anti-interference ability, and long transmission distance, making it particularly suitable for long-distance and large-scale security deployment scenarios.
Technical advantages
1. Long distance transmission capability: Cáp quang phân tán technology adopts optical signal transmission, which has advantages such as long transmission distance and low attenuation. Even at distances of tens or even hundreds of kilometers, it can maintain signal stability and clarity, meeting the needs of long-distance defense.
2. High sensitivity monitoring: Distributed fiber optic sensors can monitor real-time changes in physical quantities such as vibration and temperature around the fiber optic, and even small disturbances can be accurately captured. This enables distributed fiber optic technology to promptly detect and alert potential security threats.
3. Strong anti-interference ability: Fiber optic, as a transmission medium, has a natural ability to resist electromagnetic interference. In complex electromagnetic environments, distributed fiber optic technology can maintain stable performance and ensure the reliable operation of safety monitoring systems.
4. Easy deployment and maintenance: Distributed fiber optic technology uses optical fibers as sensors, without the need for additional cables or installation of other equipment, reducing deployment costs and maintenance difficulties. Meanwhile, the durability of optical fibers also ensures the long-term stable operation of the system.
Kịch bản ứng dụng
Border line security monitoring: In long-distance and large-scale security deployment scenarios such as border lines, distributed fiber optic technology can monitor the security status of border lines in real time, detect and report illegal border crossing behaviors in a timely manner.
Oil and gas pipeline protection: Distributed fiber optic technology can monitor real-time changes in parameters such as vibration and temperature around the pipeline, timely detect potential safety hazards, such as poaching and destruction, and ensure the safe operation of oil and gas pipelines.
Smart grid security monitoring: In the smart grid, distributed fiber optic technology can monitor changes in the surrounding environment in real time, timely detect and handle potential security risks, and ensure the stable operation of the power grid
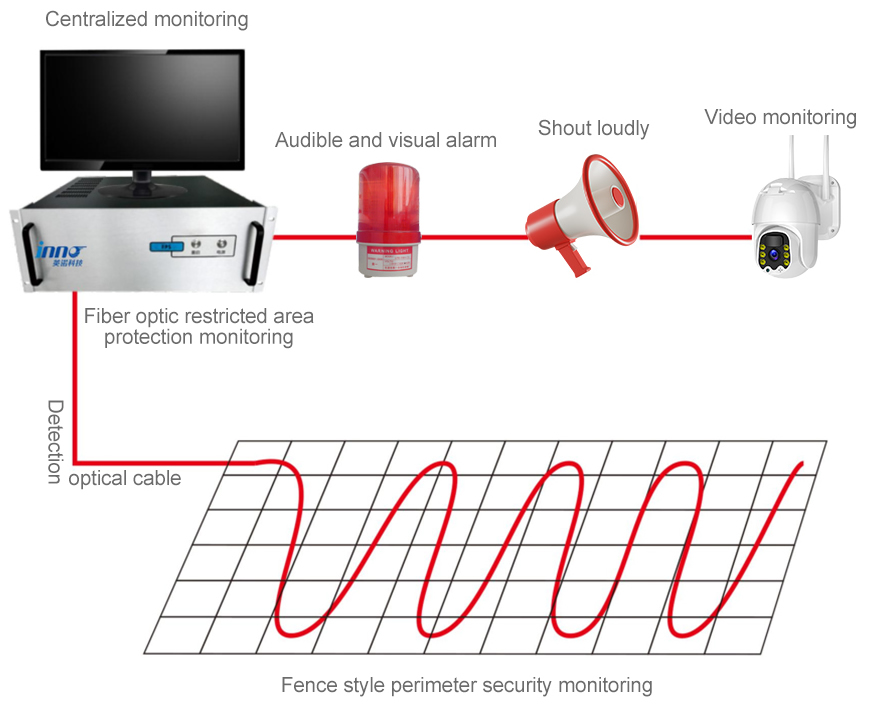
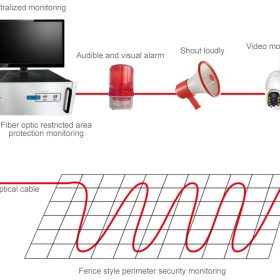
Photos of on-site installation of distributed fiber optic perimeter monitoring system

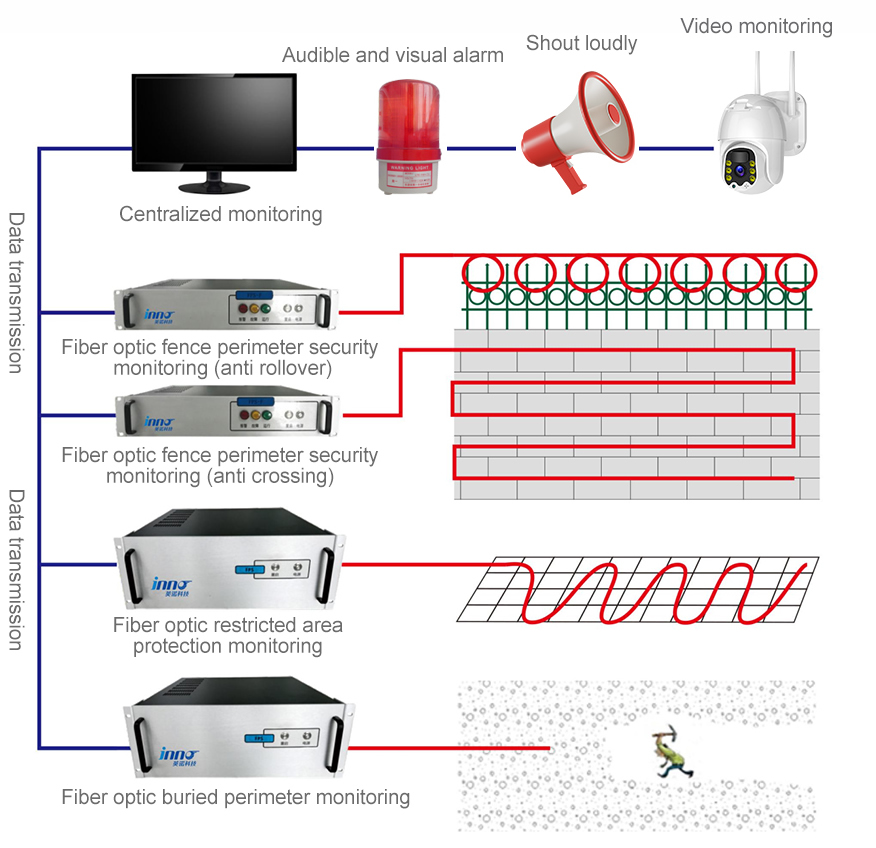
This system can be widely applied in important places to prevent intrusion, important engineering to prevent damage, important resources to prevent theft, early warning of dangerous events, monitoring and troubleshooting of communication resources, and other fields. Specific examples are as follows:
1. Intrusion prevention in important locations: perimeter security, illegal intrusion, and illegal crossing monitoring in areas such as oil, hóa dầu, chemicals, power plants, prisons, banks, museums, airports, radar stations, Cổng, border lines, scenic spots, military bases, ammunition depots, and large villa areas;
Typical Applications of Distributed Fiber Optic Vibration Sensing System
2. Important engineering damage prevention: illegal construction monitoring such as excavation by excavators and pile drivers near underground comprehensive pipe galleries, rãnh cáp, communication fiber optic cable tunnels, subway tunnels, v.v;
3. Important resource theft prevention: illegal excavation of oil and gas pipelines, drilling for oil and gas theft, and monitoring of pipeline leaks; Power cable theft prevention, v.v;
Typical Applications of Distributed Fiber Optic Vibration Sensing System
4. Early warning of dangerous events: early warning of geological hazards such as landslides and tunnel collapses; Train operation status monitoring, early warning of rigid structure damage such as tracks;
5. Monitoring and troubleshooting of communication resources: monitoring of communication fiber optic cable lines, troubleshooting of line routing, v.v.
 Cảm biến nhiệt độ sợi quang INNO ,Hệ thống giám sát nhiệt độ.
Cảm biến nhiệt độ sợi quang INNO ,Hệ thống giám sát nhiệt độ.